|
What is
a Tax Deferred Exchange?
A tax deferred exchange
is simply a method by which a property owner trades one
property for another without having to pay any federal
income taxes on the transaction. In an ordinary sale
transaction, the property owner is taxed on any gain
realized by the sale of the property. But in an exchange,
the tax on the transaction is deferred until some
time in the future, usually when the newly acquired property
is sold.
These exchanges are
sometimes called "tax free exchanges" because the exchange
transaction itself is not taxed.
Tax deferred
exchanges are authorized by Section 1031 of the Internal
Revenue Code. The requirement of Section 1031 and other
sections must be carefully met, but when an exchange is done
properly, the tax on the transaction may be deferred.
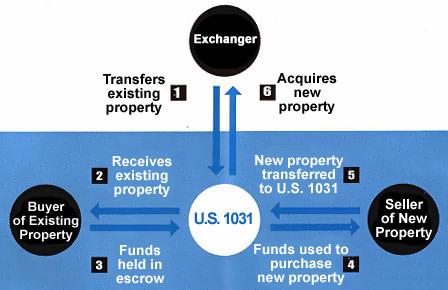
In an exchange, a
property owner simply disposes of one property and acquires
another property, rather than the sale of one property and
the purchase of another.
Today, a sale and a
reinvestment in a replacement property are converted into an
exchange by means of an exchange agreement and the services
of a qualified intermediary - a fourth party who helps to
ensure that the exchange is structured properly.
The IRS' new
regulations make exchanging easy, inexpensive and safe.
Internal Revenue Code
(IRC) Section 1031 is one of the last remaining tax
loopholes. It is a powerful tool that allows investors to
exchange any investment property for any other investment
property. For your exchange to be valid, you must follow
specific IRS regulations.
Here is an
abbreviated list of the regulations
1.) The properties
being exchanged must be of a like kind. For example, you may
exchange:
- a house for
another house (or several houses)
- a house for
commercial real estate
- land for rental
property
- a strip mall for
an office building
- any investment
property for any other investment property (as long as it
is not occupied as your primary residence)
2.) You must identify
and close on your replacement property within a specific
period of time
3.) 100% of the
proceeds from your current property must be held by a
Qualified Intermediary and applied toward your replacement
property to get a full tax deferral
4.) Your replacement
property must be of equal or greater value to the property
you have sold to get a full tax deferral
5.) Properties being
exchanged must be used for investment. Personal residences
are not exchangeable
Why use
a 1031 exchange:
To
defer your capital gains tax
To diversify
-
Exchange one property for a larger one.
-
Exchange one property for several properties.
-
Increase depreciation.
To
simplify
-
Exchange several properties for fewer (or one) property.
-
Improve the quality of your property.
-
Decrease management responsibility.
To
relocate
-
Exchange for a property closer to where you live.
-
Exchange to an area with higher appreciation.
Please
consult your tax advisor
Investing -
Interest Rates -
Moving -
Finding Best Agent
-
More Investment Information
-
Refinancing -
Selling Mistakes -
Buying Strategies
-
1031
Exchange -
Agency Information
|



